Work with git in RStudio
Below are point and click steps you can use to sync with your new GitHub repo in RStudio. You can also use the command line.
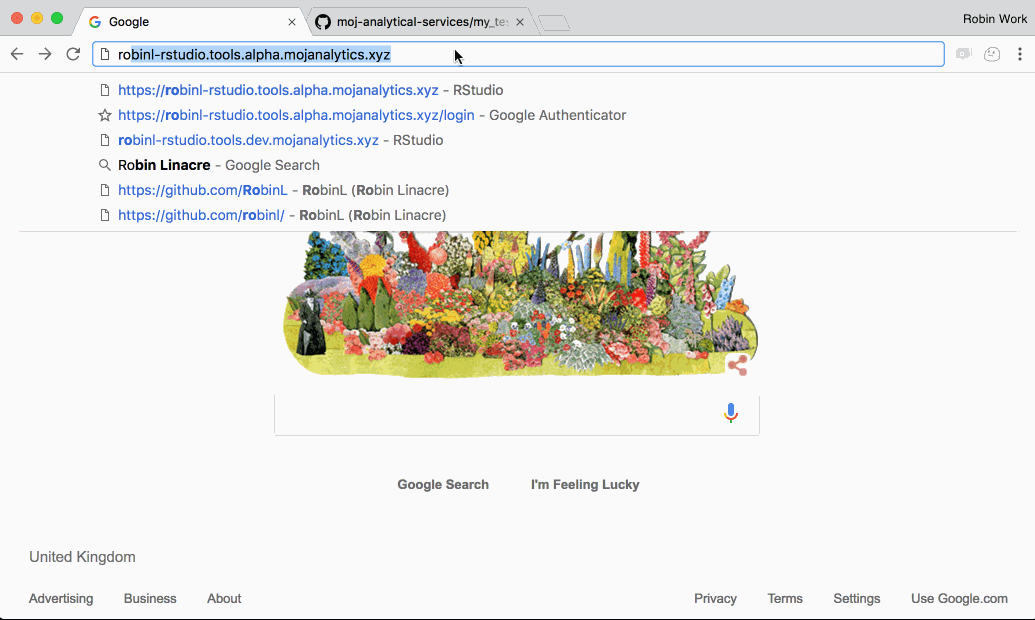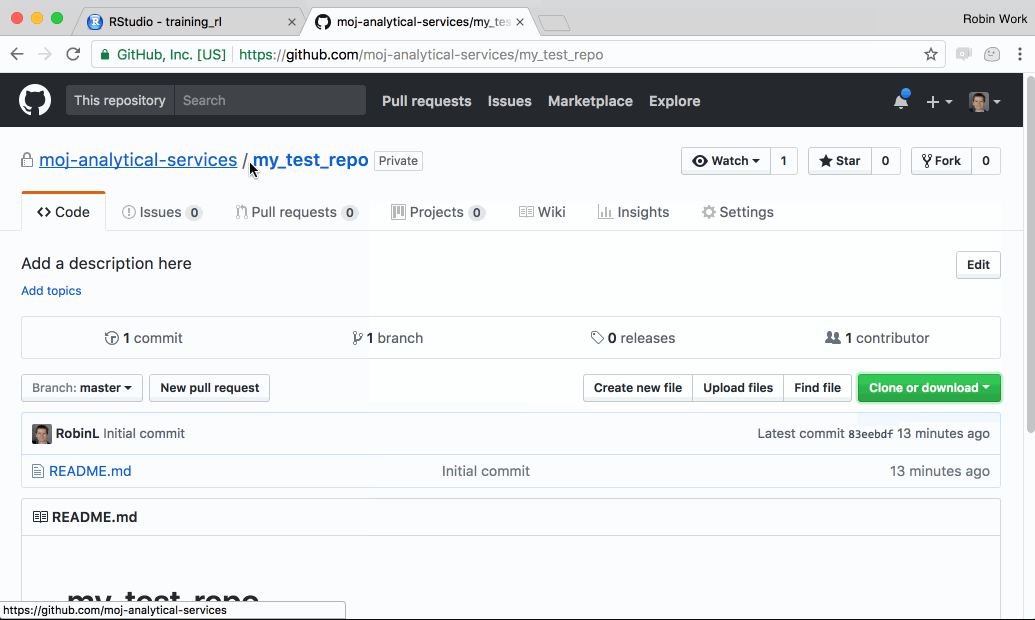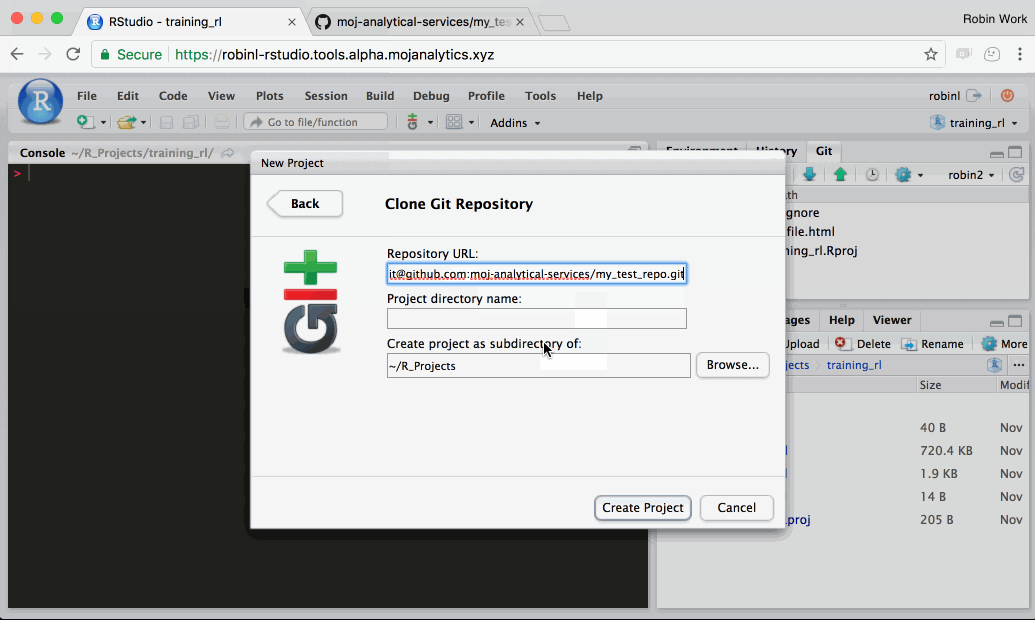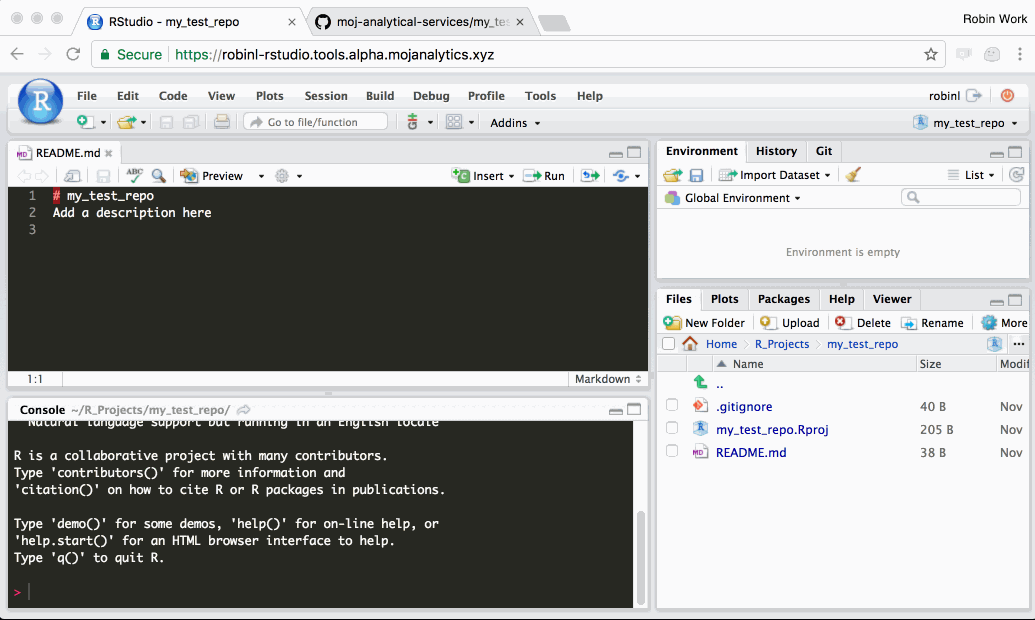
Step 1: Navigate to your platform R Studio and make a copy of the Github project in your R Studio
In this step, we create a copy of the definitive GitHub project in your personal R Studio workspace. This means you have a version of the project which you can work on and change.
Follow the steps in this gif: (Note: we now recommend making repositories Internal which is not shown in this gif)
Notes:
- When you copy the link to the repo from Github, ensure you use the ssh link, which starts
git@github.comas opposed to the https one, which startshttps://github.com/. - If this is your first time cloning a repo from Github you may be prompted to answer if you want to continue. Type yes and click enter.
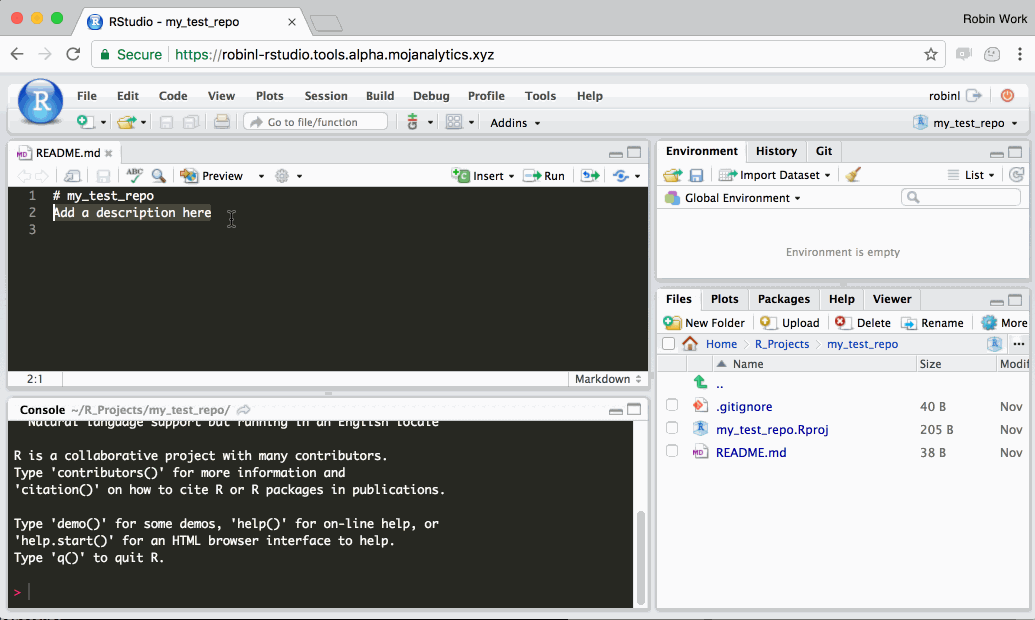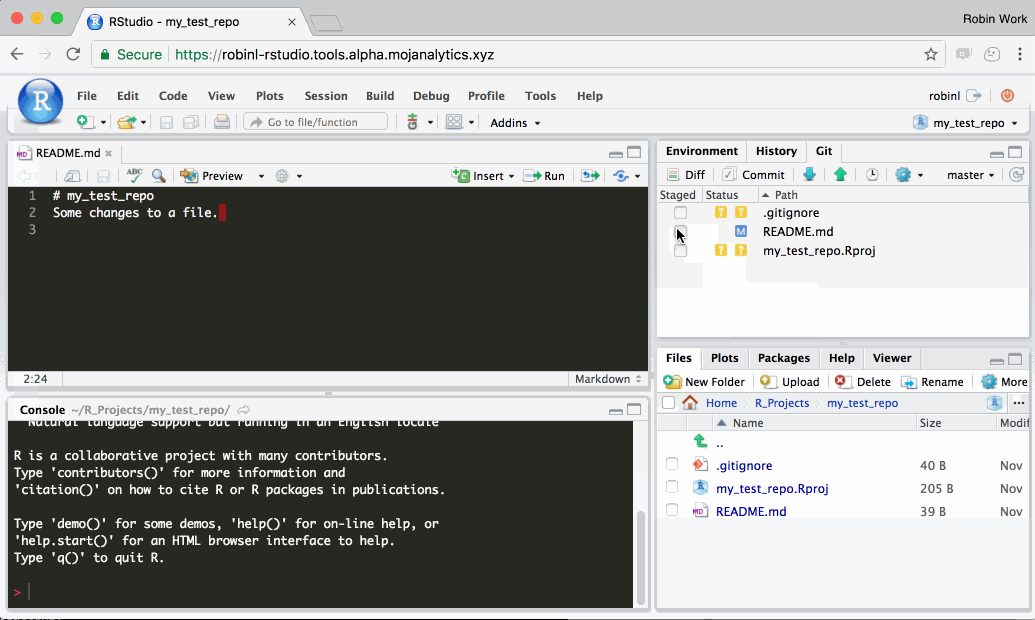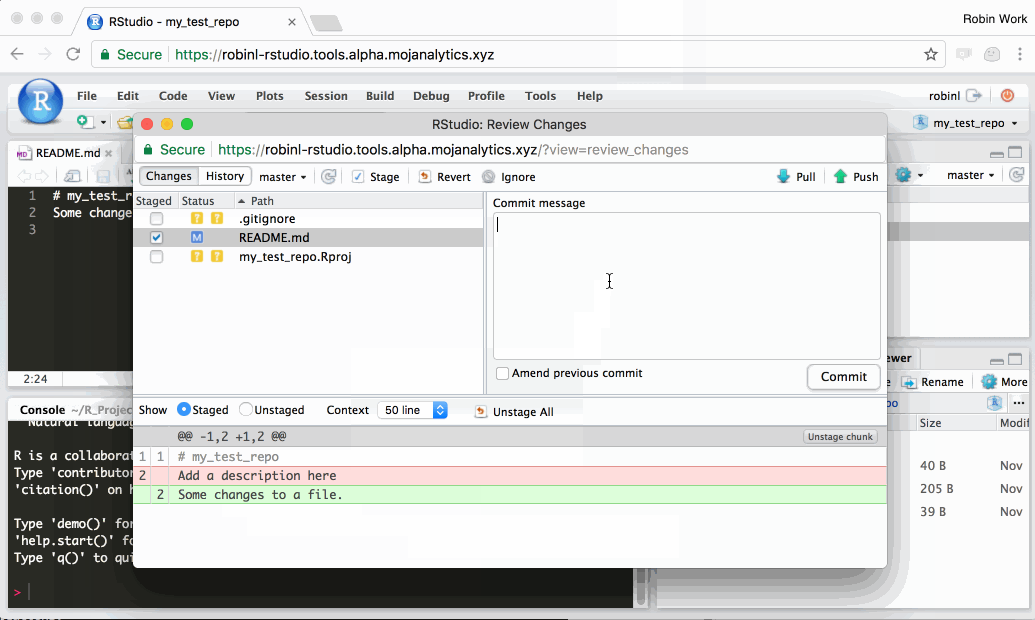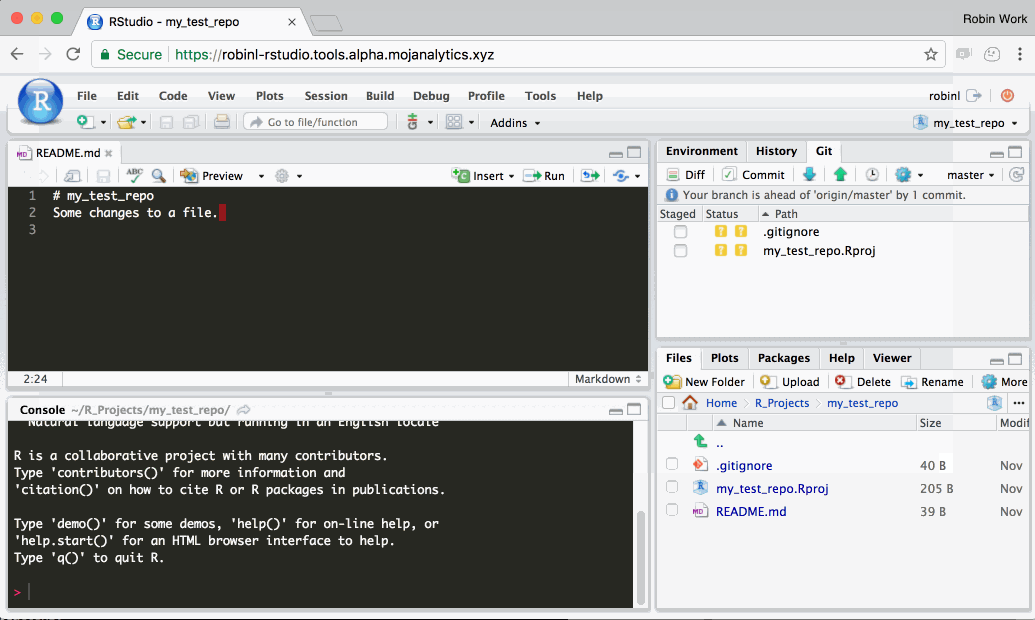
Step 2: Edit your files and track them using Git
Edit your files as usual using R Studio.
Once you’re happy with your changes, Git enables you to create a ‘commit’. Each git commit creates a snapshot of your personal files on the Platform. You can can always undo changes to your work by reverting back to any of the snapshots. This ‘snapshotting’ ability is why git is a ‘verson control’ system.
In the following gif, we demonstrate changing a single file, staging the changes, and committing them. In reality, each commit would typically include changes to a number of different files, rather than the single file shown in the gif.
Notes:
- ‘committing’ does not sync your changes with github.com. It just creates a snapshot of your personal files in your platform disk.
- Git will only become aware of changes you’ve made after you’ve saved the file as shown in the gif. Unsaved changes are signified when the filename in the code editor tab is red with an asterisk.
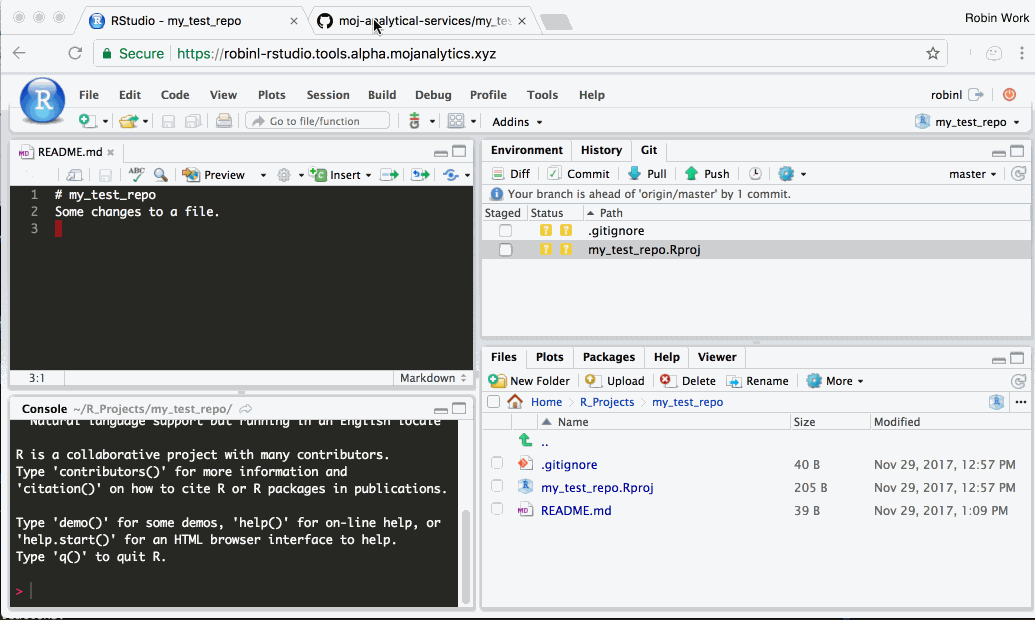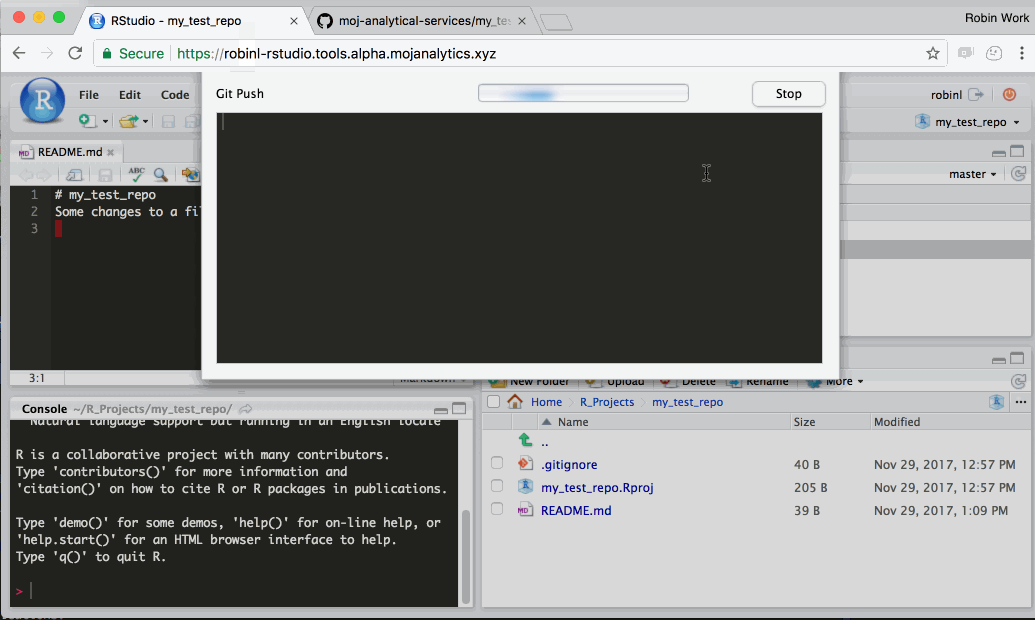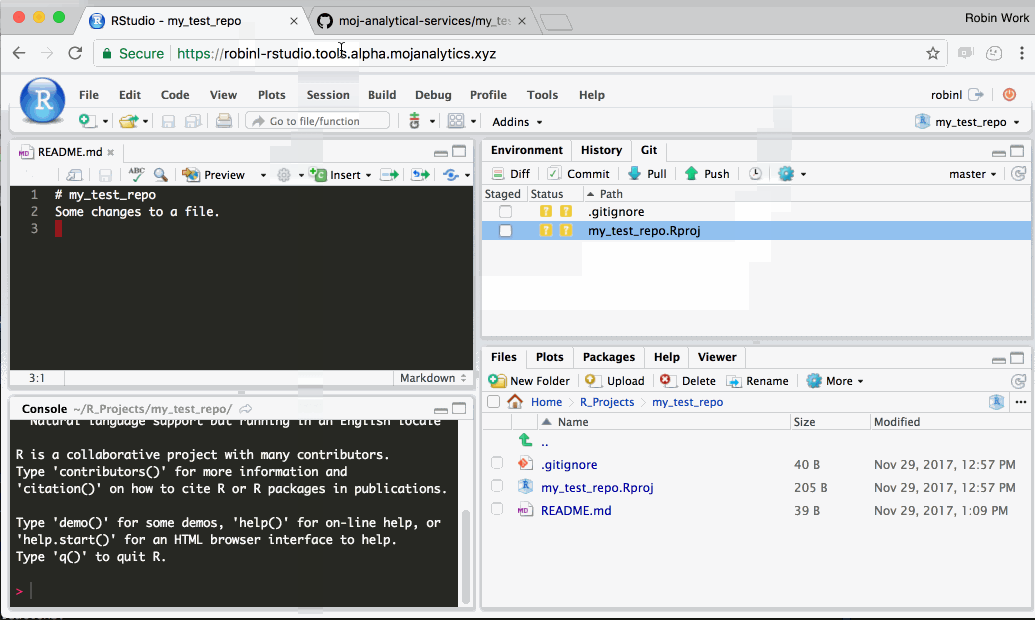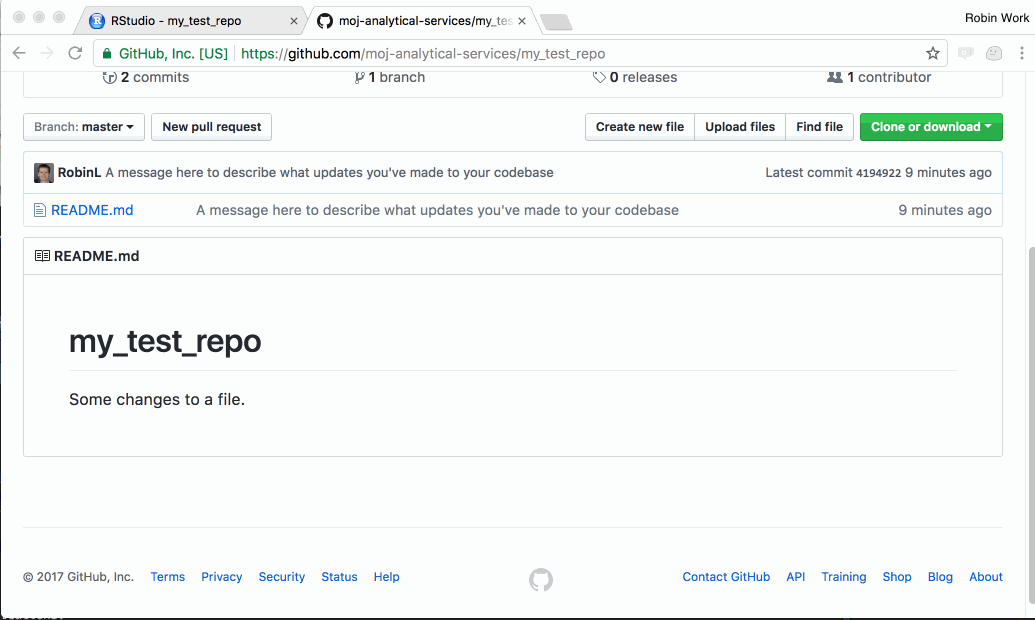
Step 3: Sync (‘push’) your work with github.com
In R Studio, click the ‘Push’ button (the green up arrow). This will send any change you have committed to the definitive version of the project on Github. You can then navigate to the project on Github in your web browser and you should see the changes.
Notes:
- After pushing, make sure you refresh the GitHub page in your web browser to see changes.
That’s it! If you’re working on a personal project, and are not collaborating with others, those three basic steps will allow you to apply version control to your work with Github