Troubleshooting Airflow Pipelines
Note that airflow time is UTC (not BST)
Manual vs Scheduled run on the UI (DAG runs are not sorted in order of when they ran but when they are scheduled. THESE ARE DIFFERENT THINGS)
Airflow will run your DAG at the end of each interval. For example, if you create a DAG with
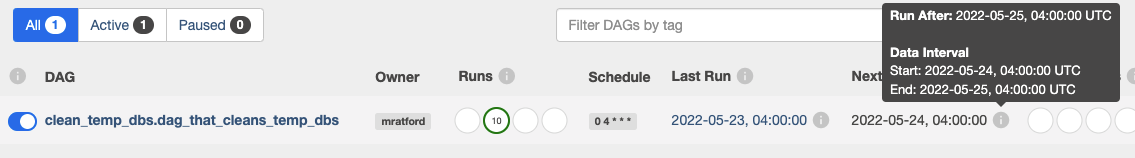
start_date=datetime(2019, 9, 30)andschedule_interval=@daily, the first run marked2019-09-30will be triggered at2019-09-30T23:59and subsequent runs will be triggered every 24 hours thereafterThis can be confusing when looking at the “Next Run” column on the UI, which gives the start time of the next interval. To find out the time when the job is next expected to run, click on the “i” which will give you the “Run After” time
Jobs using the high-memory nodes will take longer to start
If you are using a package manager such a
renv,venv, orpackrat, you will need to ensure this environment is created inside a folder that you have runchmodon (we would recommend this be yourWORKDIR).There are a limited number of nodes, so your job might be queued until a node becomes available
If your job fails, you can click on individual tasks to get more info - Clicking on the ‘logs’ button will give you access to the logs for all 4 attempts at running your code. This may help you diagnose what exactly your DAG is doing that is causing a failure. This will also give you the specific error message your DAG is producing, which will help us with diagnosis if you need to raise the issue with a data engineer.
If you get the following error message in your logs:
Pod took too long to startit’s likely that the pod is trying to pull an image that doesn’t exist so eventually times out. Have a look at the github action in your image repo (not airflow repo) to make sure it was successful and the image was built and pushed to ECR